[TOC]
安装
直接CDN引入
开发环境版本:<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
生产环境版本:<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
基本语法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| <div id="app">
<div>
{{message}}
</div>
<ul>
<!--拿到遍历对象的内容和下标-->
<li v-for="(item,index) in movies">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
<button v-on:click="add">
+
</button>
<button @click="sub">
-
</button>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
name:'wjy',
counter:0,
movies:['第一部','第二部','第三部','第四部']
},
methods:{
add:function(){
console.log("add被执行");
this.counter++;//内部调用需要加this
}
sub:function(){
console.log("sub被执行");
}
}
})
</script>
|
el:string | HTMLElement
data:Object | Function
methods:{[key:string]:Function}
mustache
Mustache语法,也就是双大括号,将data中的文本数据插入到HTML中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| <div id="app">
<div>
<h3>
{{message}}
</h3>
<h3>
{{firstName+lastName}}
</h3>
<h3>
{{firstName+' '+lastName}}
</h3>
</div>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
firstName:'ddd',
lastName:'sss'
})
</script>
|
v-once,v-html,v-text,v-pre,v-cloak
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| <style>
[v-cloak]{
display:none;
}
</style>
<div id="app" v-cloak>
<!-- 当 vue开始解析就会去掉v-cloak属性 -->
<div>
<h3>
{{message}}
</h3>
<h3 v-once>
{{message}}
</h3>
<h3>
{{url}}
</h3>
<h3 v-html="url"></h3>
<!--识别html文档-->
<h3 v-html="v-text">你好啊</h3>
<!-- xxx 使用v-text会有覆盖现象-->
<h3 v-pre>{{message}}</h3>
<!-- 打印{{message}} -->
</div>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
url:'<a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度一下</a>'
})
</script>
|
加上v-once之后,即使在控制台改app.message='111',但是页面上显示的依旧是xxx ,表明改元素和组件只渲染一次,不会随着数据的改变而改变
v-bind
动态绑定某些属性,比如类名或者style
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <div id="app">
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx'
},
computed:{
}
})
</script>
|
计算属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| <div id="app">
<h2>
{{fullName}}
<!--计算属性不需要加小括号-->
</h2>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
books:[
{id:110,name:"第一本",price:119},
{id:111,name:"第二本",price:120},
{id:112,name:"第三本",price:121},
{id:113,name:"第四本",price:122}
],
firstName:'111',
lastName:'222'
}
computed:{
//filter/map/reduce
totalPrice:function(){
let result - 0;
for(let i in this.books){
result += this.books[i].price;
}
return result;
}
fullName:{
set:function(newValue){
//一般没有set方法,将计算属性设置为可读属性,使用set方法:控制台输入app.fullName = 'gggg'就会将这个值赋给newValue
console.log(newValue);//gggg
}
get:function(){
return this.firstName+lastName;
}
}
//上下两种fullName效果相同
fullName:function(){
return this.firstName+lastName;
}
}
})
</script>
|
计算属性相较于methods性能会更好,计算属性会进行缓存,如果多次使用时,计算属性只会调用一次
v-on
作用:绑定事件监听器
缩写:@
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| <div id="app">
<!--如果该方法不需要额外参数,那么方法后面的()可以不添加
如果该方法需要一个参数,那么没有加小括号的情况下,会默认将原生事件event参数传递进去-->
<button v-on:click="add">
+
</button>
<!--需要event参数同时需要其他参数的情况下,使用$event可以拿到event参数-->
<!--字符串记得加单引号-->
<button @click="sub('fff',$event)">
-
</button>
<div @click="divClick">
<button @click.stop="btnClick">
按钮/阻止事件冒泡
</button>
</div>
</div>
<script src="../js/vue.js">
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
name:'wjy',
counter:0,
movies:['第一部','第二部','第三部','第四部']
},
methods:{
add(){
console.log("add被执行");
this.counter++;//内部调用需要加this
}
sub(abc,event){
console.log("sub被执行");
console.log(abc,event);
}
}
})
</script>
|
修饰符的使用:
.stop阻止事件冒泡.prevent阻止默认事件.{keyCode|keyAlias} 只当事件是从特定键触发时才触发回调,例: @keyup.enter="keyUp"监听回车键.native监听组件根元素的原生事件.once只触发一次回调
v-if,v-else,v-else-if
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| <div id="app">
<h2 v-if=isShow>
{{message}}
</h2>
<h1 v-else>
isShow为false时,显示我
</h1>
<!--不推荐使用v-else-if,直接用计算属性更方便-->
<h2 v-if="score>=90">优秀</h2>
<h2 v-else-if="score>=80">良好</h2>
<h2 v-else-if="score>=60">及格</h2>
<h2 v-else>不及格</h2>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'nihaoa',
isShow: false,
score:99
}
})
</script>
|
input有复用问题,会对某一些元素进行复用,如果确实需要创建新的元素的话可以用key值加以区别。
v-show
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <h2 v-if="false" id="aaa">
{{message}}<!--不会出现在DOM元素中-->
</h2>
<h2 v-show="isShow" id="bbb">
{{message}}<!--出现在DOM元素中,但display为none-->
</h2>
|
v-for
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| <!--需要中间插入值的时候,使用key属性可以更高效-->
<!--遍历数组-->
<!--不需要下标值-->
<ul>
<li v-for="item in movies" :key:"item">
{{item}}
</li>
</ul>
<!--需要下标值-->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in movies">
{{index+1}}{{item}}
</li>
</ul>
<!--遍历对象-->
<!--一个参数:value-->
<ul>
<li v-for="item in movies">
{{item}}
</li>
</ul>
<!--(value,key)-->
<ul>
<li v-for="(value,key) in movies">
{{key}}-{{value}}
</li>
</ul>
<!--(value,key,index)-->
<ul>
<li v-for="(value,key) in movies">
{{index+1}}-{{key}}-{{value}}
</li>
</ul>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
info:{
name:'ddd',
age:18,
height:1.88
},
movies:['第一部','第二部','第三部','第四部']
}
})
</script>
|
直接通过数组下标进行修改的话,并不会响应式,不会重新渲染页面
解决:
- Vue方法:set(要修改的对象,索引值,修改后的值) 响应式方法
Vue.set(this.movies,0,'第五部');
splice()
数组中的响应式方法: (使用它们改变数组也会发生对应的更新)
过滤器
| 过滤器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <div>
{{item.price}} | showPrice
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
item:{
price:11,
id:11,
num:11
}
filters:{//过滤器
showPrice(price){
return '¥' + price.toFixed(2)
}
}
}
})
</script>
|
for循环
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
for(let i in this.books){
const book = this.books[i];
totalPrice += books.price*book.count;
}
for(let item of this.books){
totalPrice += item.price*item.count;
}
let newArr = arr.filter(function(n){
return n < 100
})
let newArr2 = newArr.map(function(n){
return n*2
})
let total = newArr2.reduce(function(preValue,n){
return preValue + n
},0)
let total = arr.filter(function(n){
return n<100
}).map(function(n){
return n*2
}).reduce(function(preValue,n){
return preValue + n
},0)
let total = arr.filter(n => n<100).map(n => n*2).reduce((pre,n)=>pre +n);
|
v-model
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <!-- v-model可以绑定input或者textarea -->
<div id="app">
<!-- v-model双向绑定 -->
<input type="text" v-model="message">
<!-- "message"会直接成为input的value,修改input里面的内容,message的值也会被改变 -->
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx'
}
})
</script>
<!--input有一个input事件-->
<div id="app">
<input type="text" :value="message" @input="message = $event.target.value">
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx'
}
}
})
</script>
|
v-model结合radio
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <!--通过v-model绑定,可以将数据传递到data里面的sex,同时v-model绑定了同一个变量这时可以省略name属性-->
<div id="app">
<label for="male">
<input type="radio" id="male" value="男" v-model="sex">男
</label>
<label for="female">
<input type="radio" id="female" value="女" v-model="sex">女
</label>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
sex:'男'//radio会默认选中男的单选框
}
}
})
</script>
|
v-model结合checkbox
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| <div id="app">
<!--单选框,对应布尔值-->
<!--加label后点击文字也可以选中复选框-->
<label for="agree">
<input type="checkbox" id="agree" v-model="isAgree">同意协议
</label>
<!--同意协议之后才能点击下一步-->
<button :disabled="!isAgree">
下一步
</button>
<!--复选框,对应数组-->
<input type="checkbox" value="爱好1" v-model="hobbies">爱好1
<input type="checkbox" value="爱好2" v-model="hobbies">爱好2
<input type="checkbox" value="爱好3" v-model="hobbies">爱好3
<input type="checkbox" value="爱好4" v-model="hobbies">爱好4
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
isAgree:false,
hobbies:[]
}
})
</script>
|
v-model结合select
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| <div id="app">
<!--单选,字符串类型-->
<select name="abc" v-model="fruit">
<option value="水果1">水果1</option>
<option value="水果2">水果2</option>
<option value="水果3">水果3</option>
<option value="水果4">水果4</option>
<option value="水果5">水果5</option>
</select>
<!--多选mutiple,数组类型-->
<select name="abc" v-model="fruits" multiple>
<option value="水果1">水果1</option>
<option value="水果2">水果2</option>
<option value="水果3">水果3</option>
<option value="水果4">水果4</option>
<option value="水果5">水果5</option>
</select>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
fruit:'水果1',//默认选择水果1
fruits:[]
}
})
</script>
|
修饰符
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <div id="app">
<!--lazy失去焦点或者敲回车的时候再进行绑定-->
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="message">
<!--v-model默认绑定过去的值都是string类型-->
<!--number-将绑定的值改为数字类型-->
<input type="text" v-model.number="message">
<!--trim将字符串左右两边的空格消除-->
<input type="text" v-model.trim="message">
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'xxx',
fruit:'水果1',//默认选择水果1
fruits:[]
}
})
</script>
|
判断图片是否加载完成
- JS方法:
img.onload
- Vue:
@load
1
| <img :src="goods.img" @load="imageLoad">
|
生命周期
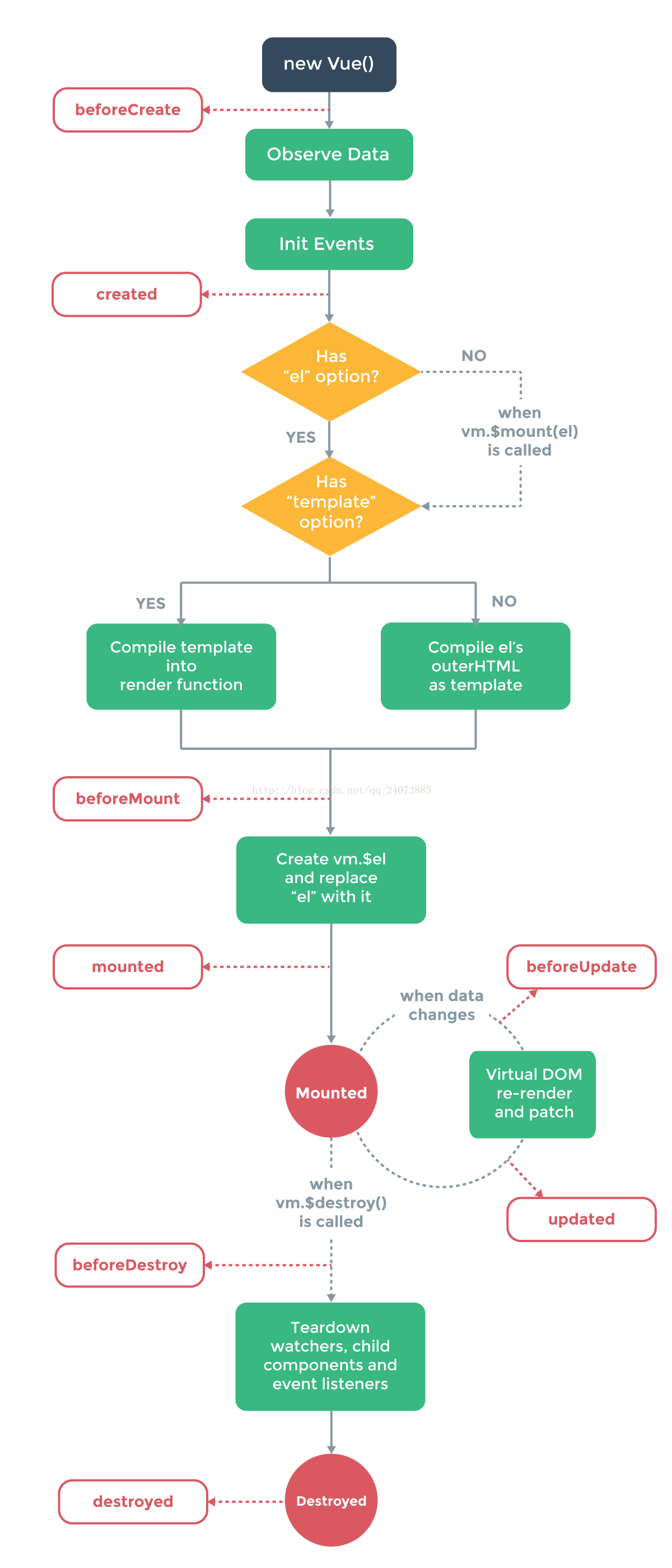
它可以总共分为8个阶段:
- beforeCreate(创建前)
- created(创建后)
- beforeMount(载入前)
- mounted(载入后)一般将vue写在这里面
- beforeUpdate(更新前)
- updated(更新后)
- beforeDestroy(销毁前)
- destroyed(销毁后)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| <div id=app>{{a}}</div>
<script>
var myVue = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
a: "Vue.js"
},
beforeCreate: function() {
console.log("创建前")
console.log(this.a)
console.log(this.$el)
},
created: function() {
console.log("创建之后");
console.log(this.a)
console.log(this.$el)
},
beforeMount: function() {
console.log("mount之前")
console.log(this.a)
console.log(this.$el)
},
mounted: function() {
console.log("mount之后")
console.log(this.a)
console.log(this.$el)
},
beforeUpdate: function() {
console.log("更新前");
console.log(this.a)
console.log(this.$el)
},
updated: function() {
console.log("更新完成");
console.log(this.a);
console.log(this.$el)
},
beforeDestroy: function() {
console.log("销毁前");
console.log(this.a)
console.log(this.$el)
console.log(this.$el)
},
destroyed: function() {
console.log("已销毁");
console.log(this.a)
console.log(this.$el)
}
});
</script>
|
组件化
- 创建组件构造器
Vue.extend()
- 注册组件
Vue.component()
- 使用组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| <div id="app">
<!--3.使用组件 -->
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
</div>
<!--组件模板抽离写法1 -->
<script type="text/x-template" id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>111111</h2>
<h2>111111</h2>
</div>
</script>
<!--组件模板抽离写法2 -->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>111111</h2>
<h2>111111</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//1.创建组件构造器对象
const cpnC = Vue.extend({
template:`#cpn` //模板抽离
})
//2.注册组件(全局组件)
Vue.component('my-cpn',cpnC);
//语法糖写法:(将一二两步合并)
Vue.component('cpn1',{
template:`
<div>
<h2>111111</h2>
<h2>111111</h2>
</div>`
})
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
/*注册局部组件
components:{
//cpn;使用组件的标签名
cpn:cpnC
}
局部组件语法糖:
components:{
'cpn1':{
template:`
<div>
<h2>111111</h2>
<h2>111111</h2>
</div>`
}
}
*/
})
</script>
|
父子组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| <script>
const cpnC1 = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>111111</h2>
<h2>111111</h2>
</div>`
})
const cpnC2 = Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>222222</h2>
<h2>2222222</h2>
</div>`,
cpmponents:{
cpn1:cpnC1
//在父组件里面注册子组件
//在这里注册作用域只在于cpnC2
}
})
//root组件
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
components:{
cpn2:cpnC2
cpn1:cpnC1
//在这里注册就可以在实例里面使用了
}
})
</script>
|
父子组件的通信
1.通过props向子组件传递数据
2.通过事件向父组件发送消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| <!--父传子-->
<div id="app">
<cpn :cmovies="movies" :cmessage="message"></cpn>
<!-- v-bind不支持驼峰标识,如果是驼峰要绑定要用横杠-写法-->
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<!--必须有一个外层div作为根元素-->
{{cmovies}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
const cpn = {
template:'#cpn',
//props:['cmovies','cmessage'],
props:{
//类型限制
cmovies: Array,
//
cmessage:{
type: String,
default:'aaaaaa'
}
//如果没有传入则cmessage的默认值为'aaaaaa'
required: true
//表示必须传入该值
}
},
data(){
return{}
}
}
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:"nnnn",
movies:['第一步','第一步','第一步'];
}
components:{
cpn
//属性的增强写法
}
})
</script>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| Vue.component('my-component',{
props{
//多个可能的值
propA:[Srting,Number],
//带有默认值的数字
propB:{
type: Number,
default:100
}
//带有默认值的对象
propC:{
type:Object,
//对象或数组的默认值必须从一个工厂函数获取
default: function(){
return{message:'hello'}
}
}
//自定义验证函数
propD:{
validator: function(value){
return ['success','warning','danger'].indexof(value) !== -1
}
}
}
})
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| <!--子传父-->
<!--父组件模板-->
<div id="app">
<!--接受子组件的事件-->
<cpn @itemclick="cpnclick"> </cpn>
</div>
<!--子组件模板-->
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<button v-for="item in categories" @click="btnclick(item)">
{{item.name}}
</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const cpn = {
template:'#cpn',
data(){
return{
categories:[
{id:'aaa',name:'第一'},
{id:'bbb',name:'第二'},
{id:'ccc',name:'第三'}
]
}
},
methods:{
btnclick(item){
//子组件发射自定义事件
this.$emit('itemclick',item)
}
}
}
//父组件
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'aaa'
},
components{
cpn
},
methods{
cpnClick(item){
concole.log('接收到子组件的事件',item)
}
}
})
</script>
|
父子组件间的访问
组件data
组件内部使用的数据需要放在自己的data,methods属性
data必须为一个函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <script>
Vue.component('cpn',{
template:'#cpn',
data(){
return{
title:'abc'
}
},
watch:{
//监听值是否有改变
name(newValue,oldValue){
//改变后执行的函数
}
}
})
</script>
|
slot
插槽的基本使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| <cpn>
<button>
会替换到slot处,只会替换没有名字的
</button>
</cpn>
<template>
<div>
<h2>
我是组件
</h2>
<slot>
<div>
我是默认值
</div>
</slot>
</div>
</template>
|
具名插槽的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <cpn>
<button slot="left">
会替换到name为left的slot处
</button>
</cpn>
<template>
<div>
<slot name="left"></slot>
<slot name="center"></slot>
<slot name="right"></slot>
</div>
</template>
|
作用域
父级模板的数据来自父组件,子级模板的数据来自子组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <div id="app">
<!--isShow数据来自挂载id=app的Vue实例的data-->
<cpn v-show="isShow"></cpn>
<!--取到的name.data就是pLanguages-->
<cpn>
<template slot-scope="name">
<span v-for="item in slot.data"></span>
</template>
</cpn>
</div>
//data name这些名字都是可以自定义的
//作用域插槽:
//父组件替换插槽的标签,内容由子组件提供
<template>
<div>
<!--如果想要拿到cpn中的data中的pLanguages值-->
<slot :data="pLanguages"></slot>
</div>
</template>
|
CommonJS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
module.exports = {
flag: true,
test(a,b){
return a+b
},
demo(a,b){
return a*b
}
}
let {test,demo,flag} = require('moduleA');
let _mA = require('moduleA');
let test = _mA.test;
let demo = _mA.demo;
|
ES模块化的导入导出
1
2
3
|
<script src="aaa.js" type="module"></script>
<script src="bbb.js" type="module"></script>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
var name="111";
var age="222";
var flag = true;
function sum(num1,num2){
return num1+num2;
}
export{
flag,sum
}
export var num1 = 1000;
export function des(num1, num2){
return num1-num2;
export class Person{
run(){
console.log('ssss');
}
}
const address = '北京';
export default address
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
import{flag,sum}from"./aaa.js";
if(flag){
console.log(sum(20,30));
}
import{Person}from"./aaa.js";
const p = new Person();
p.run();
import add from"./aaa.js";
import * as item from './aaa.js'
console.log(item.name);
|
webpack
1
2
3
4
5
|
require('./css/normal.css')
requiree('./css/special.less')
|
ES6和CommonJS的导出文件不可以写在同一个文件里面
Vue CLI
安装cnpm:
cnpm: npm install -g cnpm –registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
使用cnpm命令来安装模块:
cnpm install [name]
安装vue脚手架:
npm install -g @vue/cli
runtime-compiler和runtime-only的区别
runtime-compiler: template -> ast -> render -> vdom ->UI
runtime-only: render -> v-dom -> UI
runtime-only:1.性能更高 2.下面的代码量更少
createElement用法
createElement('标签',{标签的属性}),['数组的内容']
createElement('h2',{class:'box'},['Hello World',createElement('button',['按钮'])])
路由器
hash
通过localtion.hash进行改变网站的url而且不会进行再次刷新和重新向服务器请求资源
pushState
history.pushState({},'','home')
压缩进一个栈,永远显示的时是在栈顶的那一个,会记住每一个历史记录
replace
history.replaceState({},'','home')
替换,不会记录每一次历史记录
go
history.go(-1) = history.back()
history.go(1) = history.forward()
往前跳一页,用数字来进行在栈里面的跳转
打包文件的解析
npm run build
dist ->static ->js
app:当前应用程序开发的所有代码(业务代码)
vwndor:提供商,比如第三方Vue,axios,bs
manifest:为了打包的代码数据做底层支撑
路由的懒加载
当打包构建应用时,js包会变得非常大,在第一次加载时影响页面的加载速度,如果我们能把不同路由的组件分割成不同的代码块,然后当路由被访问时才会加载对应的组件。这样加载会更加的高效,提高用户的体验舒适度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| const routes = [
{
path: '/home',
components: () => import('../cpmponents/Home')
}
]
|
路由传递参数
两种类型
params动态路由
配置路由格式:/router/:id
传递方式:在path后面跟上对应的值
传递后形成的路径:/router/123
query
配置路由的格式:/router,也就是普通配置
传递的方式:对象中使用query的key作为传递方式
传递后形成的路径:/router?id=123
拿参数:this.id = this.$route.params.id
两种使用方式
- 代码修改
- router-link
导航守卫
监听页面跳转
meta 元数据(描述数据的数据)
metaclass 元类
全局守卫:
router.beforeEach 前置守卫 页面跳转前发生,调用next函数可以跳到指定页面
router.afterEach 后置钩子 页面跳转后发生,不需要主动调用next()函数
路由独享守卫:…
组件内的守卫:…
vue-router-keep-alive
两个属性
include 字符串或者正则,只有匹配的组件会被缓存
exclude 字符串或者正则,任何匹配的组件都不会被缓存
Promise
一般情况下有异步操作的话,使用Promise对异步操作进行封装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
},1000)
}).then(() => {
console.log("1111111");
return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
})
}).then(() => {
console.log("222222");
return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
})
}).then(() => {
console.log("3333333333");
})
})
})
new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject('error message')
},1000)
}).then(() => {}).catach((err) => {
console.log(err)
})
new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('aaa')
},1000)
}).then(res => {
console.log("......");
return Promise.resolve(res + '111')
}).then(res => {
console.log(".......")
})
new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('aaa')
},1000)
}).then(red => {
console.log("......");
return res + '111'
}).then(res => {
console.log(".......")
})
|
Promise 的 all方法使用
使用该方法可以再所有的网络请求都结束之后再进行then方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| Promise.all([
new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
$ajax({
url:'url1',
success: function(data){
resolve(data)
}
})
}),
new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
$ajax({
url: 'url2',
success: function(data){
resolve(data)
}
})
})
]).then(results => {
results[0]
results[1]
} )
|
Vuex
1.安装vuex插件并使用
2.创建对象const store = new Vuex.store({}) 并在state里面定义状态
3.在其他页面使用e.g. 拿到定义的couter状态
4.定义方法:在mutations里面进行定义,必须是同步操作
5.在需要使用这个方法的页面的method进行commit this.$store.commit('mutation里面定义的方法名')就可以啦
6.当有异步操作的时候,方法要先放在actions里面然后放在mutations里面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| mutation: {
updateInfo(state){
}
}
actions: {
aUpdateInfo(context,payload) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('updateInfo');
console.log('payload')
},1000)
}
}
|
在需要使用这个方法的页面的method进行commit this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo','我是payload')就可以啦
如果一开始address属性不在state中定义,
添加:state.info['address'] = '洛杉矶'不会被显示,因为这个时候不是响应式,而需要要用Vue.set(state.info,'address','洛杉矶')就会变成响应式。
删除:
delete state.info.age没有响应式
Vue.delete(state.info,'age')有响应式
推荐将mutations里面的方法名字使用常量代替,之后在store和method里面要用到这个方法名的话直接使用这个常量
Vuex getter
Vuex里面的计算属性
1
2
3
4
5
| getters: {
fullname(state){
return state.name + '11111'
}
}
|
Vuex modules
将需要的模块可以放在modules,而每一个模块都可以拥有自己的state,mutation,actions,getter
使用方法:
$store.state.a.name
拿到模块a里面的state里面的name状态
this.$store.commit('updateName','lisi)
commit:模块和mutations的上传方式都一样
axios
1.进行安装:npm install axios –save
2.在项目中进行导入:import axios from 'axios'
3.直接使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata',
method: 'get',
params: {
type: 'pop',
page: 1
}
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
})
|
axios发送并发请求与全局配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://123.207.32.32:8000'
axios.defaults.timeout = 5000
axios.all([
axios({
url: '/home/multidata'
}),
axios({
url: '/home/data'
})
])then(axios.spread((res1,res2) => {
console.log(res1);
console.log(res2);
}))
|
get请求对应params
post请求对应data
axios的实例和模块封装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| const instance2 = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://,,,,'
timeout:5000
})
instance1({
url:'/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
})
instance1({
url:'/home/data'
}).then({
res => {
console.log("这是使用这个实例的第二个方法")
}
})
|
一般使用第三方框架的时候不要直接进行引用,进行模块封装之后再进行使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
|
import axios from 'axios'
export function request(config,success,failure) {
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://....'
timeout: 5000
})
instance(config)
.then(
res =>{
console.log(res);
success(res)
}
)
.catch(
err =>{
console.log(err)
failure(err)
}
)
}
import {request} from "./network/request";
request(
{
url: '/home/multidata'
},
res => {
console.log(res)
},
err => {
console.log(err)
}
)
export function request(config) {
return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http......'
timeout: 5000
})
instance.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
console.log(config)
return config
},
err => {
console.log(err)
})
instance.interceptors.response.use(
res => {
console.log(res)
return res
},
err => {
}
)
return instance(config)
})
}
request({
url: '/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err)
})
|
axios拦截器
用于在发送每次请求或者得到回应之后,进行相应的处理
事件总线
当两个部分距离太远互相之间没有联系但是需要传输数据的时候,可以使用事件总线
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue()
methods: {
imageLoad() {
this.$bus.$emit('itemTmageLoad',参数)
}
}
created() {
this.$bus.$on('itemTmageLoad', () => {
Done;
})
}
|
$emit('事件名称',参数)
$on('事件名称',回调函数(参数))
刷新频繁的防抖操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| debounce(func,delay) {
let timer = null
return function (...args) {
if(timer){
clearTimerout(timer)
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(this,args)
},delay)
}
}
const refresh = this.debounce(this.$refs.scroll.refresh,500)
|
:el
所有的组件都有一个$el:属性,用于获取组件中的元素
